Navigating the landscape of web development interviews requires a solid grasp of core concepts, practical skills, and emerging technologies. Whether you’re a fresh graduate or a seasoned professional, preparing with comprehensive questions and nuanced answers can give you a significant edge. This guide covers fundamental topics like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frameworks, databases, and deployment strategies, ensuring you are well-equipped for any technical interview scenario.
Understanding the intricacies of front-end and back-end development, along with the latest trends such as server-side rendering and cloud integration, is vital. Additionally, familiarizing yourself with tools like Git, CI/CD pipelines, and web security practices enhances your readiness. Throughout this discussion, relevant authoritative resources are referenced, such as detailed insights into creating unique digital experiences through custom web design, which can help you deepen your understanding of designing user-centric websites.
This compilation aims not just to prepare you for interview questions but also to foster a comprehensive understanding of modern web development practices, making you a valuable candidate for top tech companies and innovative startups alike.
1. What is HTML and Why Is It Essential in Web Development?
HTML, or HyperText Markup Language, serves as the foundational building block for creating web pages and applications. It uses a structured system of tags and attributes to define various parts of a webpage, including headings, paragraphs, links, images, and multimedia content. For example, the <p> tag signifies a paragraph, while <a> establishes hyperlinks. These tags instruct the browser on how to display and organize content effectively.
HTML’s role extends beyond mere structuring; it forms the backbone for accessibility, SEO, and the integration of multimedia elements. As web technologies evolve, understanding HTML remains crucial for building responsive, semantic, and accessible websites. For a deeper grasp of how custom web design can help create engaging user experiences, you might explore resources on creating unique digital experiences.
2. How Do HTML Tags Function, and What Are Their Types?
HTML tags are the core syntax elements used to mark up content within a webpage. They are enclosed within angle brackets, like <tag>, and typically come in pairs: an opening <tag> and a closing </tag>. These tags define the beginning and end of an element, guiding the browser on how to interpret the content inside.
Self-closing tags, such as <img> or <br>, do not require a closing counterpart and are used for elements like images or line breaks. Proper understanding of tags ensures semantic correctness and enhances accessibility. In web development, choosing the right tags and structuring them properly also supports better SEO practices, which are critical for business growth, as discussed in why custom web design outperforms templates.
3. What Are the Key Differences Between HTML and XHTML?
| Feature | HTML | XHTML |
|————————|—————————————————|—————————————————|
| Tag Syntax | Can be uppercase or lowercase; flexible. | Must strictly be lowercase. |
| Document Type Declaration | Optional, not always required. | Requires a <!DOCTYPE html> declaration at the start. |
| Parsing | More forgiving, tolerant of errors. | Stricter, enforces syntax rules like proper nesting. |
| Namespace Support | Does not support XML namespaces. | Supports XML namespaces for better integration. |
| Self-Closing Tags | Optional slash (<br>). | Must include slash (<br />). |
Understanding these differences is vital when developing standards-compliant and compatible websites, especially for projects requiring XML integration or stricter validation.
4. What Are Semantic HTML Elements and Why Are They Important?
Semantic HTML elements clearly describe their purpose within the webpage, improving both accessibility and SEO. Elements like <header>, <footer>, <article>, <section>, <nav>, and <aside> provide meaningful structure to the document, making it easier for screen readers and search engines to interpret content correctly.
Using semantic tags enhances user experience by enabling assistive technologies to navigate content logically. For instance, a well-structured <header> indicates the start of a section or page, while <article> encapsulates a standalone piece of content. For insights into creating accessible and user-friendly sites, see how custom web design can elevate accessibility.
5. Why Is the <!DOCTYPE html> Declaration Important?
The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration informs the browser about the version of HTML being used, ensuring the page renders in standards mode. This consistency is crucial for maintaining predictable behavior across different browsers and devices. Since HTML5 simplifies this declaration, placing <!DOCTYPE html> at the very beginning of your document signals compliance with modern web standards.
Proper declaration helps avoid quirks mode, which can cause inconsistent rendering and bugs. For developers aiming to craft standards-compliant websites that perform reliably, mastering this aspect is fundamental.
6. How Do Block-Level and Inline Elements Differ?
Block-level elements occupy the full width of their container and begin on a new line, creating a block of content. Examples include <div>, <p>, <h1>–<h6>, and <section>. Inline elements, such as <span>, <a>, and <img>, only take up as much width as necessary and flow within the surrounding content without breaking the line.
Understanding these distinctions allows developers to control layout and spacing effectively. For complex layouts, modern CSS techniques like Flexbox and Grid are often combined with block and inline elements to create responsive designs.
7. What Is CSS, and How Does It Enhance Web Pages?
CSS, or Cascading Style Sheets, is the language responsible for the visual presentation of web pages. It controls layout, colors, fonts, spacing, and responsiveness, enabling developers to separate content from design. This separation facilitates easier updates and ensures consistency across a website.
CSS can be embedded directly in HTML via <style> tags, included inline within elements, or linked as external stylesheets using the <link> tag. To understand how custom web design elevates branding and user engagement, explore designing for unique digital experiences.
8. What Are the Different Methods to Integrate CSS into a Webpage?
There are three main ways to incorporate CSS:
-
Inline CSS: Applying styles directly to individual elements via the
styleattribute, e.g.,<p style="color: blue;">. -
Internal CSS: Embedding style rules within a
<style>block inside the<head>section. -
External CSS: Linking an external stylesheet with
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">. This method promotes reusability and easier maintenance across multiple pages.
Choosing the appropriate method depends on project size, reusability needs, and performance considerations.
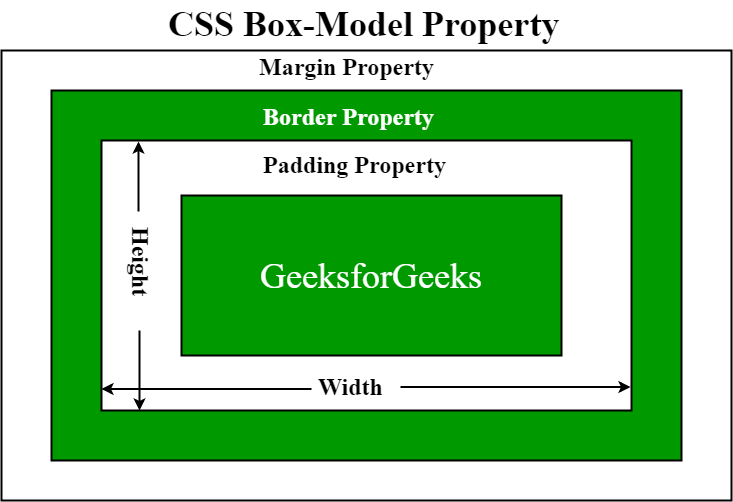
9. What Is the CSS Box Model and Why Is It Fundamental?
The CSS box model describes how every HTML element is represented as a rectangular box comprising four parts:
-
Content: The actual text or media.
-
Padding: Space between content and border.
-
Border: Surrounds the padding and content.
-
Margin: Space outside the border, separating the element from others.
Understanding the box model is critical for layout control, as total element size is calculated by adding content size, padding, border, and margin. For a visual explanation, refer to the box model diagram.
10. How Do Class and ID Selectors Differ in CSS?
| Aspect | Class Selector (.classname) | ID Selector (#idname) |
|————————|—————————————————–|————————————————–|
| Usage | Applied to multiple elements. | Unique to a single element. |
| Specificity | Lower specificity. | Higher specificity. |
| Reusability | Reusable across many elements. | Should be unique per page. |
| Example | .btn { color: red; } | #header { background-color: blue; } |
Using classes promotes consistency and reusability, while IDs are ideal for targeting specific elements for unique styling or scripting.
11. What Are CSS Flexbox and Grid, and When Should You Use Them?
Flexbox is a one-dimensional layout module that aligns and distributes space among items in a container, making it ideal for arranging items in a row or column, especially when their sizes are dynamic. For example:
css
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
CSS Grid provides a two-dimensional layout system, allowing placement of items in rows and columns simultaneously. It is suitable for complex, grid-based designs:
css
.container {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);
grid-gap: 10px;
}
Both systems enhance layout flexibility compared to traditional float-based designs.
12. What Is the Difference Between Padding and Margin in CSS?
Padding is the space between the content of an element and its border, affecting the internal spacing. Margin is the space outside the element’s border, creating separation between neighboring elements. Adjusting padding affects the size of the element, while margin influences layout positioning and spacing.
13. What Is JavaScript, and Why Is It Vital for Web Interactivity?
JavaScript is a high-level programming language that adds dynamic behavior to websites. It enables functionalities like form validation, real-time updates, animations, and asynchronous data loading (AJAX). JavaScript runs in the browser (client-side) and on servers (via Node.js), making it essential for full-stack development.
To explore how custom web design enhances user engagement, consider creating unique digital experiences.
14. How Do let, const, and var Differ in JavaScript?
| Keyword | Reassignment | Scope | Hoisting | Mutability of Value | Usage Tips |
|———|—————-|——–|———–|———————|————|
| var | Yes | Function/global | Yes | Mutable | Declare variables with function scope. |
| let | Yes | Block | No | Mutable | Recommended for block scope. |
| const | No | Block | No | Immutable (binding), but objects can be modified | Best for constants or references that shouldn’t change. |
Understanding these differences helps write predictable, bug-free code, especially in large applications.
15. What Is the DOM, and How Does It Facilitate Web Interaction?
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programmable interface representing the structure of HTML and XML documents as a tree of nodes. It allows scripts (like JavaScript) to dynamically access, modify, add, or remove elements, enabling interactive and responsive websites. For example, changing the text of a <p> element or adding new menu items involves DOM manipulation.
16. What Is Event Delegation, and Why Is It Useful?
Event delegation involves attaching a single event handler to a parent element instead of multiple handlers to individual child elements. When an event occurs on a child, it bubbles up to the parent, where it can be handled efficiently. This approach reduces memory usage and simplifies code, especially for dynamically added elements.
javascript
document.getElementById('parent').addEventListener('click', function(event) {
if (event.target && event.target.matches('button.className')) {
// Handle button click
}
});
17. How Do JavaScript Promises Manage Asynchronous Operations?
Promises are objects representing the eventual outcome of an asynchronous task. They have three states: pending, fulfilled, or rejected. Promises allow chaining (then) and error handling (catch), resulting in cleaner code compared to nested callbacks.
“`javascript
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(‘Success!’), 1000);
});
promise.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
“`
18. What Is the Difference Between == and === in JavaScript?
==(abstract equality) compares values after type coercion, which can lead to unexpected results:
javascript
5 == '5'; // true
0 == false; // true
===(strict equality) compares both value and type without coercion:
javascript
5 === '5'; // false
0 === false; // false
Using === is generally recommended for predictable comparisons.
19. How Do Closures Work in JavaScript?
A closure is created when an inner function retains access to variables from its outer scope even after the outer function has finished executing. Closures enable data encapsulation and private variables.
“`javascript
function outerFunction() {
let secret = ‘hidden’;
function innerFunction() {
console.log(secret);
}
return innerFunction;
}
const reveal = outerFunction();
reveal(); // ‘hidden’
“`
20. What Does the this Keyword Represent in JavaScript?
this refers to the context in which a function is invoked:
- In the global scope,
thispoints to the window object. - Inside a method, it refers to the owning object.
- In constructors, it points to the new instance.
- In event handlers, it refers to the element that triggered the event.
- Arrow functions inherit
thisfrom their lexical scope, not their invocation context.
21. What Is an Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE)?
An IIFE is a function that runs immediately after its definition, typically used to create a private scope.
javascript
(function() {
var privateVar = 'I am private';
console.log(privateVar);
})();
Variables inside an IIFE do not pollute the global namespace, helping prevent conflicts and maintaining encapsulation.
22. How Do Arrow Functions Differ from Traditional Functions?
Arrow functions provide a concise syntax and inherit this from their surrounding scope. They cannot be used as constructors and lack a prototype.
“`javascript
const sum = (a, b) => a + b;
const obj = {
value: 10,
arrowFunc: () => console.log(this.value),
regularFunc: function() { console.log(this.value); }
};
obj.arrowFunc(); // undefined
obj.regularFunc(); // 10
“`
They are ideal for short functions and when lexical this is desired.
23. What Is REST in JavaScript?
The rest operator (...) allows functions to accept an indefinite number of arguments as an array.
javascript
function sumAll(...numbers) {
return numbers.reduce((total, num) => total + num, 0);
}
It simplifies handling variable argument lists and enhances function flexibility.
24. What Is AJAX, and How Is It Used?
AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) enables web pages to fetch data asynchronously without reloading. It uses the XMLHttpRequest object or the fetch API to communicate with servers and update parts of the UI dynamically.
javascript
fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
Using JSON instead of XML streamlines data handling and improves performance.
25. What Are Web APIs and Their Role in Modern Web Development?
Web APIs provide interfaces for browsers and servers to enable functionalities like DOM manipulation, geolocation, graphics, and offline support. Examples include:
- DOM API: Access and modify webpage content.
- Fetch API: Make network requests.
- Geolocation API: Access user location.
- Canvas API: Render graphics.
For more on how APIs enhance web experiences, see creating engaging digital experiences.
26. What Is CORS, and Why Is It Important?
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a browser security feature restricting web pages from requesting resources from different domains unless explicitly permitted. The server uses headers like Access-Control-Allow-Origin to specify allowed origins.
For example:
http
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://example.com/
Proper CORS configuration ensures secure cross-origin interactions, vital for APIs and web services.
27. How Does Responsive Web Design Enhance User Experience?
Responsive design adapts webpage layouts to various device sizes using flexible grids, images, and media queries. This guarantees optimal viewing, navigation, and interaction on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Sample media query:
css
@media (min-width: 600px) {
body { font-size: 18px; }
}
Implementing responsiveness is essential for modern web usability and SEO, fostering better engagement and retention.
28. What Is React, and How Does It Facilitate UI Development?
React is a JavaScript library focusing on building reusable, component-based user interfaces. It employs a virtual DOM to optimize rendering, improving performance in dynamic applications.
Key features include JSX syntax, component lifecycle methods, state management, and props for data passing.
jsx
function HelloWorld() {
return <h1>Hello, World!</h1>;
}
React streamlines development of interactive and scalable web apps.
29. What Is Angular, and What Are Its Core Features?
Angular is a comprehensive framework for creating single-page applications using TypeScript and HTML. Developed by Google, it offers features like:
- Two-way data binding
- Dependency injection
- Modular architecture
- Built-in directives and services
An example component:
typescript
@Component({
selector: 'app-hello',
template: `<h1>Hello, Angular!</h1>`
})
export class HelloComponent {}
Angular supports enterprise-grade web solutions with robust tooling.
30. How Does Vue.js Support UI Development?
Vue.js is a progressive framework that simplifies building interactive interfaces. Its reactive data binding, component system, and directives make development straightforward.
Sample component:
“`vue
Hello, Vue!
“`
Vue’s flexibility and performance make it popular for small to large projects.
31. What Is Node.js, and Why Is It Popular?
Node.js is a runtime environment enabling JavaScript execution outside browsers. Its event-driven, non-blocking architecture is ideal for scalable network applications.
Features include:
- Asynchronous I/O
- Rich package ecosystem via NPM
- Built-in modules like HTTP, File System
Sample server:
javascript
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.end('Hello from Node.js');
});
server.listen(3000);
Node.js empowers full-stack development with JavaScript.
32. What Is Express.js and How Does It Simplify Server-Side Coding?
Express.js is a minimalist web framework for Node.js that streamlines server creation. It provides routing, middleware support, and templating.
Example:
“`javascript
const express = require(‘express’);
const app = express();
app.get(‘/’, (req, res) => res.send(‘Hello, Express!’));
app.listen(3000);
“`
Express enhances productivity and maintains clean, modular codebases.
33. How Do Props and State Function in React?
Props are read-only inputs passed from parent to child components, enabling data sharing. State manages internal component data, mutable over time, typically via hooks like useState.
Example:
jsx
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}!</h1>;
}
Proper use of props and state is critical for dynamic, interactive React applications.
34. How Does the Virtual DOM Improve React Performance?
React’s virtual DOM is a lightweight copy of the real DOM in memory. When state changes, React updates this virtual DOM, calculates differences (diffing), and applies only the necessary changes to the actual DOM. This process minimizes costly DOM manipulations, resulting in faster UI updates.
35. What Are Higher-Order Components (HOCs) in React?
HOCs are functions that take a component and return an enhanced version with additional features. They promote code reuse and abstraction.
Example:
jsx
function withLogger(WrappedComponent) {
return function(props) {
console.log('Rendering:', WrappedComponent.name);
return <WrappedComponent {...props} />;
};
}
They are useful for adding functionalities like authentication or logging across multiple components.
36. What’s the Difference Between SQL and NoSQL Databases?
| Aspect | SQL (Relational) | NoSQL (Non-Relational) |
|——————-|——————————————|——————————————|
| Data Model | Tables with fixed schemas | Flexible, document, key-value, graph |
| Schema | Enforced, predefined | Dynamic, schema-less |
| Scalability | Vertical (scale-up) | Horizontal (scale-out) |
| Transactions | Supports ACID | Limited, eventual consistency |
| Use Cases | Banking, ERP, enterprise systems | Real-time analytics, flexible schemas |
Choosing between them depends on application needs.
37. How Does Node.js Handle I/O Operations Efficiently?
Node.js employs an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. It registers callbacks for asynchronous operations, allowing the main thread to process other tasks while waiting for I/O completion. The event loop manages these operations seamlessly, supporting high concurrency without multithreading.
38. What Is Middleware in Express.js? Examples and Usage
Middleware functions have access to request (req), response (res), and next middleware in the chain. They can perform logging, authentication, parsing, and error handling.
Example:
javascript
app.use(express.json()); // Parses JSON request bodies
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url}`);
next();
});
Middleware enhances modularity and code manageability.
39. How Do SQL and MongoDB Differ? Use Cases and Key Features
| Feature | SQL Databases | MongoDB |
|————————–|—————————————|—————————————–|
| Data Structure | Structured tables | JSON-like flexible documents |
| Schema | Rigid schema | Schema-less |
| Transactions | Full ACID support | Limited, document-level atomicity |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling | Horizontal scaling |
| Joins | Supported | Not supported; denormalization common |
| Use Cases | Banking, ERP, analytics | Real-time apps, rapid prototyping |
Select based on project complexity and data flexibility needs.
40. How Do Indexes in MongoDB Improve Query Performance?
Indexes in MongoDB are data structures that allow quick location of documents matching query criteria, significantly reducing search time. By indexing key fields, queries can bypass full collection scans, leading to faster retrieval especially in large datasets.
41. How Are HTTP Methods Used in a MERN Stack Application?
- GET: Fetch data (e.g., retrieve user info).
- POST: Create new data (e.g., register users).
- PUT: Update existing data.
- DELETE: Remove data.
These methods facilitate CRUD operations through API endpoints, forming the backbone of data interaction in MERN applications.
42. How Do Authentication and Authorization Work in MERN?
Authentication verifies user identity (e.g., login with JWT). Authorization controls access to resources based on roles or permissions. Middleware handles these processes, ensuring only authorized users access sensitive routes, vital for secure applications.
43. What Is Server-Side Rendering (SSR), and How Does It Benefit React Apps?
SSR renders React components on the server, sending fully generated HTML to clients. Benefits include faster initial load times, improved SEO, and better user experience, especially important for content-heavy sites. Frameworks like Next.js facilitate SSR in React-based projects.
44. What’s the Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS?
| Feature | HTTP | HTTPS |
|———————–|—————————————-|————————————-|
| Security | Data in plain text | Encrypted via SSL/TLS |
| Port | 80 | 443 |
| Data Privacy | Not secure | Secure, data confidentiality assured |
| Usage | General browsing, less sensitive data | E-commerce, online banking, login pages |
Implement HTTPS for protecting user data and maintaining trust.
45. Why Is Version Control Using Git Essential?
Git manages code changes, supports collaboration, branching, and history tracking. It enables multiple developers to work simultaneously, resolve conflicts, and revert to previous versions if needed, ensuring project stability and efficient teamwork.
46. What Are CI/CD Pipelines, and How Do They Improve Development?
CI/CD involves automatically integrating code changes, running tests, and deploying updates. This automation reduces manual errors, accelerates releases, and maintains high-quality code. Visual tools and scripts streamline the entire process, supporting continuous improvement.
47. What Is NPM, and How Does It Support Node.js Development?
NPM (Node Package Manager) is the default package manager for Node.js, providing access to a vast ecosystem of reusable modules. It simplifies installing, updating, and managing dependencies, greatly speeding up development workflows.
48. How Do You Ensure Cross-Browser Compatibility?
Strategies include feature detection, using vendor prefixes, applying polyfills, and testing across multiple browsers and devices. Modern frameworks and tools also abstract browser inconsistencies, easing compatibility challenges.
49. What Is CSRF, and How Can It Be Prevented?
Cross-Site Request Forgery tricks authenticated users into unwanted actions. Prevention techniques include implementing CSRF tokens, validating request origins via headers, and setting cookies with SameSite attributes, thereby safeguarding user sessions.
50. How Do You Optimize Web Application Loading Speed?
- Compress images and assets.
- Use external CSS and JavaScript files with caching.
- Minify code to reduce size.
- Implement lazy loading for images.
- Minimize redirects and HTTP requests.
- Enable browser caching and content delivery networks (CDNs).
These practices ensure faster, more responsive websites, enhancing user satisfaction and SEO rankings.