An efficient and well-structured web architecture is fundamental to delivering high-quality digital products that meet both user expectations and business objectives. It acts as a detailed plan guiding data flow, security measures, and user experience, ensuring your application performs reliably under various conditions. A thoughtfully designed architecture not only enhances performance and security but also simplifies future modifications, scalability, and integration of new features. As the web landscape evolves, understanding the core principles and emerging trends in application architecture becomes crucial for developers and businesses aiming to stay competitive.
Building a robust web application requires clarity on its core components, layered structures, and the different models and types available. From single-page applications to microservices, each architectural style offers unique benefits suited to specific project needs. Incorporating best practices and leveraging advanced tools ensures that your application remains scalable, secure, and adaptable. Additionally, staying informed about modern trends like caching systems, serverless computing, and content delivery networks (CDNs) can significantly enhance your application’s responsiveness and efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamental concepts of web application architecture, examine various architectural models, and discuss the latest trends shaping the future of web development. Whether you’re a startup founder or an experienced developer, understanding these principles will empower you to design applications that are not only functional but also resilient, scalable, and aligned with your business goals.
What is Web Application Architecture?
Web application architecture serves as a strategic blueprint that defines how different components of an application interact to deliver a seamless user experience. It maps out the relationships between user interfaces, servers, databases, middleware, and other infrastructure elements, ensuring that each part functions harmoniously. Essentially, it provides a logical layout that clarifies how data flows between the client and server, optimizing performance, security, and maintainability.
Think of it as the architectural design of a building—laying out the structure, load-bearing elements, and utility systems to ensure the building’s stability and usability. In web development, this blueprint guides developers in creating scalable and efficient applications that can adapt to changing requirements and user loads.
Web Application Architecture Diagram
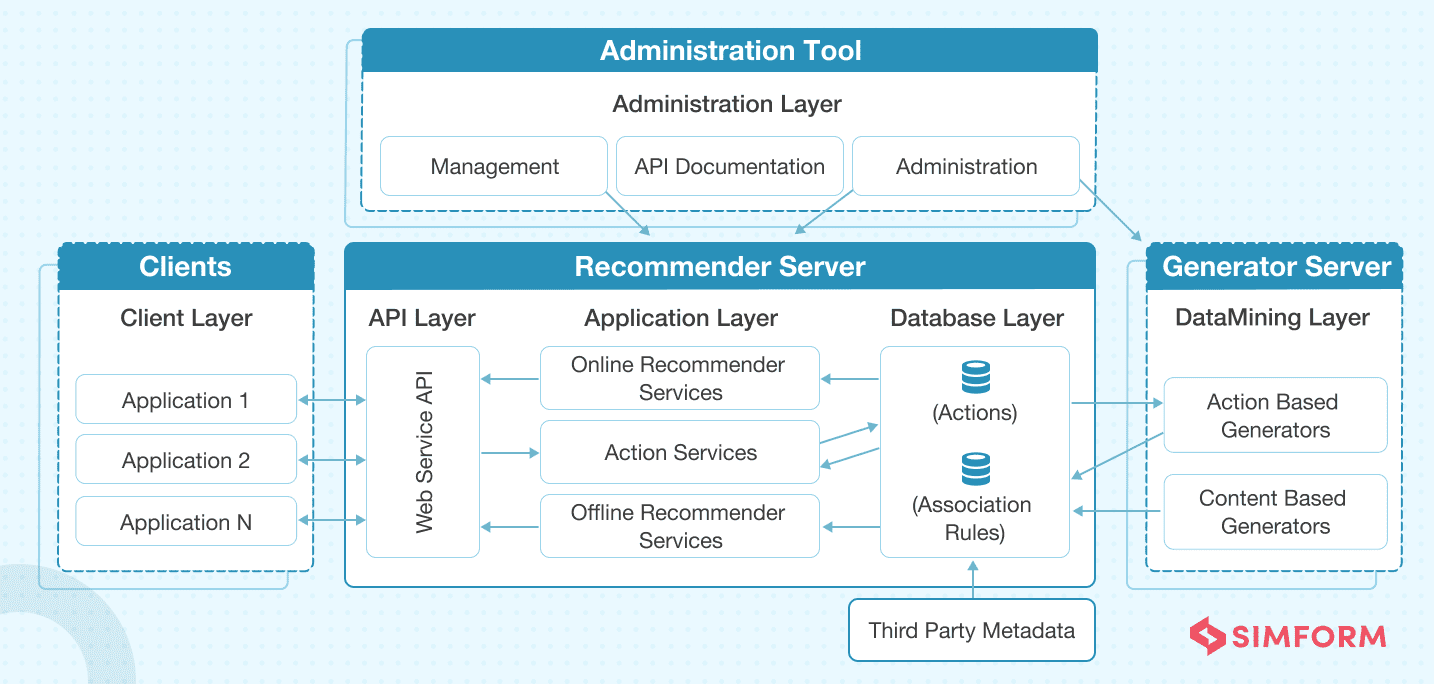
This diagram illustrates the interconnected components that comprise a typical web application, including clients, servers, databases, and middleware, highlighting how they communicate to deliver content and services.
Why is Web App Architecture Important?
The significance of a solid web app architecture cannot be overstated. As user expectations rise and market dynamics shift rapidly, a flexible and resilient architecture becomes essential to maintain competitive advantage. Without a proper framework, your application risks becoming a tangled “big ball of mud,” leading to increased development costs, poor performance, and security vulnerabilities.
A well-designed architecture provides multiple benefits:
- Performance Optimization: Efficient handling of both static and dynamic content ensures quick load times and smooth interactions.
- Scalability: As your user base grows, your application can scale seamlessly without major overhauls.
- Modular Development: Breaking down the system into smaller, independent modules accelerates development and simplifies testing.
- Enhanced Security: Dividing the application into secure blocks minimizes vulnerability exposure.
- Ease of Maintenance: Clear separation of concerns makes updates and feature additions more manageable.
- Future-Proofing: An architecture that accommodates emerging technologies ensures longevity and adaptability.
By adopting best practices and staying abreast of trends such as progressive web apps (PWAs) and serverless architectures, you can build resilient systems capable of evolving with technological advances. For example, exploring the diverse applications of JavaScript reveals how versatile frontend and backend development can be.
How Does Web App Architecture Function?
At its core, web application operation hinges on two primary components:
- Client-side (Frontend): Developed using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, this is the interactive part of the application that runs in the browser, handling user inputs and displaying content.
- Server-side (Backend): Responsible for processing requests, executing business logic, and interacting with databases, typically written in languages like Java, PHP, Ruby, or Python.
An additional crucial element is the database server, which stores and retrieves data as requested by the backend. Proper understanding of server-side rendering and scripting is vital for optimizing performance and security.
How It Works in Practice
When a user types a URL into their browser, such as “walmart.com,” the browser initiates a request to the Domain Name System (DNS) to resolve the domain into an IP address. The request then reaches the web server hosting the site, which processes it and fetches the necessary data from the database or other storage systems. The server responds by sending back the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript needed to render the page, which the browser then displays to the user.
For more insights into building scalable web applications, refer to this guide on scalable architectures.
Layers of Web App Architecture
Modern web applications often adopt a layered architecture comprising:
- Presentation Layer (Client): Handles user interface and interaction.
- Business Logic Layer: Processes data, enforces rules, and manages workflows.
- Persistence Layer: Manages data storage and retrieval, often linked to databases.
- Database Layer: Stores structured data securely and efficiently.
Smaller applications might combine some layers, while large, complex applications may have additional subdivisions. This layered approach ensures modularity, making it easier to develop, test, and maintain each part independently.
Visual Representation
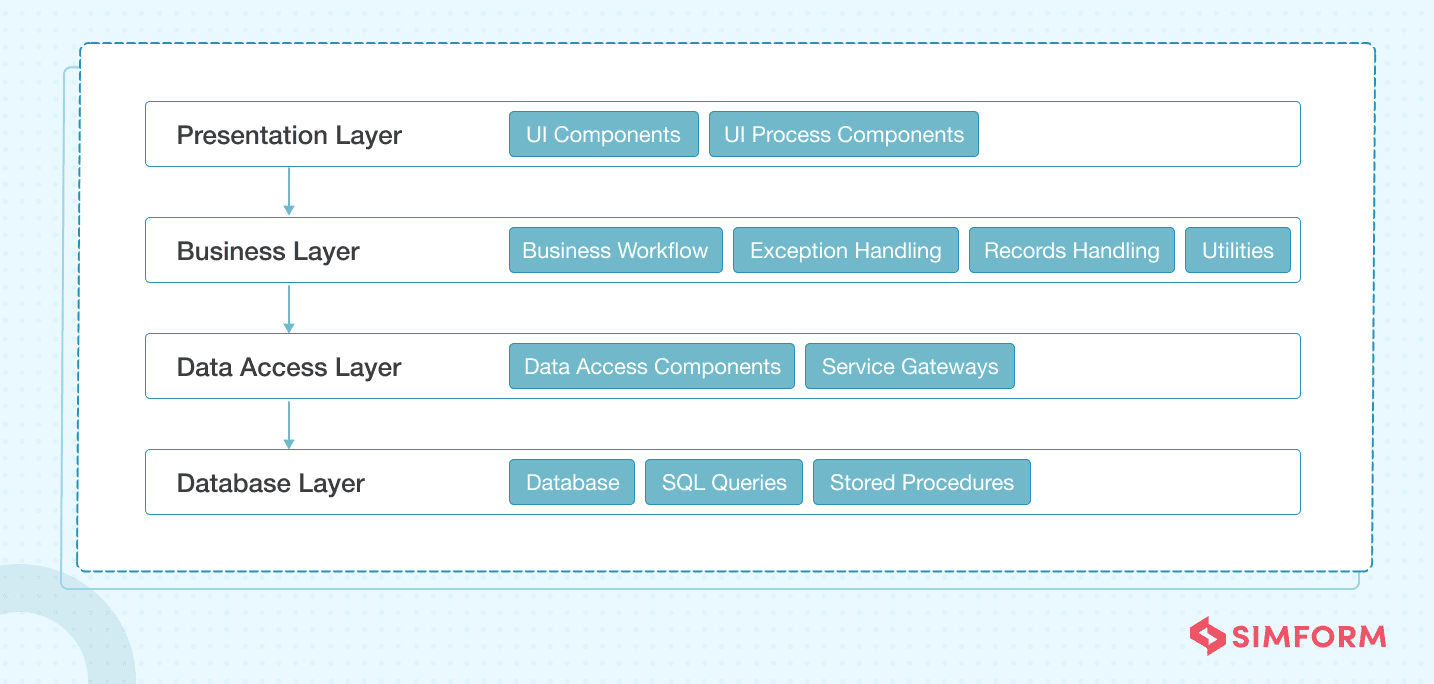
Each layer functions separately, interacting through well-defined interfaces, which allows for independent development and easier updates without disrupting the entire system.
Web Application Components
Web app components are generally categorized into:
- User Interface Elements: Visual components like dashboards, notifications, and activity logs that enhance user experience but do not directly influence system architecture.
- Structural Components: Comprising client-side elements such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, and server-side elements like web servers and databases.
On the server side, frameworks like Node.js, Django, or Ruby on Rails facilitate the creation of robust backend services, ensuring smooth communication with databases and external APIs.
Models of Web Applications
Selecting the appropriate architecture model is critical to achieving optimal performance and scalability. Common models include:
- Single Server with Single Database: Suitable for testing or small-scale projects but offers limited redundancy.
- Multiple Servers with Single Database: Enhances reliability by distributing load but may still face bottlenecks if the database becomes a single point of failure.
- Multiple Servers with Multiple Databases: Provides high resilience and performance through data replication and distribution.
Each model serves different scales and complexity levels, and choosing the right one depends on your application’s specific needs and growth plans.
Types of Web Application Architecture
Choosing the right architecture pattern depends on your application’s requirements. The main types include:
1. Single Page Application (SPA)
SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update content as users interact, resulting in a seamless experience akin to native apps. They leverage JavaScript frameworks like Angular or React, shifting most logic to the client side. This approach improves responsiveness and reduces server load.
For instance, building engaging SPAs can significantly enhance user satisfaction.
2. Microservice Architecture
This model decomposes applications into small, loosely coupled services that communicate via APIs. It simplifies development, deployment, and maintenance, enabling teams to work independently on different modules. Companies like Netflix and Amazon frequently utilize microservices to support scalable, resilient applications.
3. Serverless Architecture
In serverless setups, cloud providers manage infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on code. This pattern enables rapid scaling and cost-effective operation, especially suited for event-driven applications. Services like AWS Lambda exemplify this approach.
Learn more about the benefits of serverless computing here.
4. Progressive Web Applications (PWAs)
PWAs combine the best of web and mobile apps, offering offline capabilities, push notifications, and easy installation. They work across browsers and devices, providing a rich experience without requiring app store downloads. Companies like Starbucks and Pinterest leverage PWAs to reach users effectively.
Web Application Architecture Best Practices & Tools
Designing robust architecture involves adhering to established principles:
- Maintain system flexibility and efficiency
- Promote component reusability
- Write clean, modular code
- Ensure high scalability and reliability
- Implement security standards
- Facilitate bug detection and user feedback collection
- Use immutable infrastructure and consistent staging environments
Tools such as IDEs (Webstorm, Github Atom), UX design platforms (Figma, Sketch), and frameworks (React, Angular, Django) support these practices.
Advanced and Scalable Web Application Architecture Trends
As technology advances, so do architectural strategies. Noteworthy trends include:
1. Caching Strategies
Implementing caching reduces database load and improves response times. Techniques include application server caches, distributed caches, global caches, and CDNs. For example, content delivery networks like CloudFront accelerate content delivery by caching assets closer to users.
2. Cloud Storage Solutions
Services like Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage offer scalable, durable storage options. They enable applications to handle large volumes of data efficiently, supporting features like versioning and lifecycle management.
3. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Utilizing CDNs such as AWS CloudFront or Azure CDN ensures fast, reliable content delivery globally, reducing latency and server load.
4. Load Balancing
Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers prevents overload and ensures high availability, whether through hardware or software load balancers.
5. Multi-Server Architectures
Adding server replicas enhances fault tolerance and scalability, crucial for high-traffic applications.
6. Message Queues
Systems like Amazon SQS or RabbitMQ facilitate asynchronous communication between services, improving scalability and decoupling components for better reliability.
Conclusion
The foundation of any successful web application lies in its architecture. As markets evolve and user demands increase, a flexible, scalable, and secure architecture becomes indispensable. Collaborating with experienced architects can help you navigate choices and implement best practices tailored to your business needs. At Simform, our team specializes in designing innovative, future-proof web architectures to empower your digital presence. Reach out today to build a web application that not only meets today’s standards but is prepared for tomorrow’s challenges.